The Sleep Paralysis Phenomenon: What Happens to Your Brain?
Imagine waking up in the middle of the night, fully conscious but unable to move or speak. You feel a strange pressure on your chest, and in some cases, you might even see a shadowy figure lurking in the room. This terrifying experience is known as sleep paralysis—a mysterious phenomenon that has puzzled scientists and frightened people for centuries.
What Is Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis is a temporary state in which a person is awake but unable to move or speak. It occurs when the brain wakes up from sleep, but the body remains in a paralyzed state. This typically lasts a few seconds to a couple of minutes before normal movement returns.
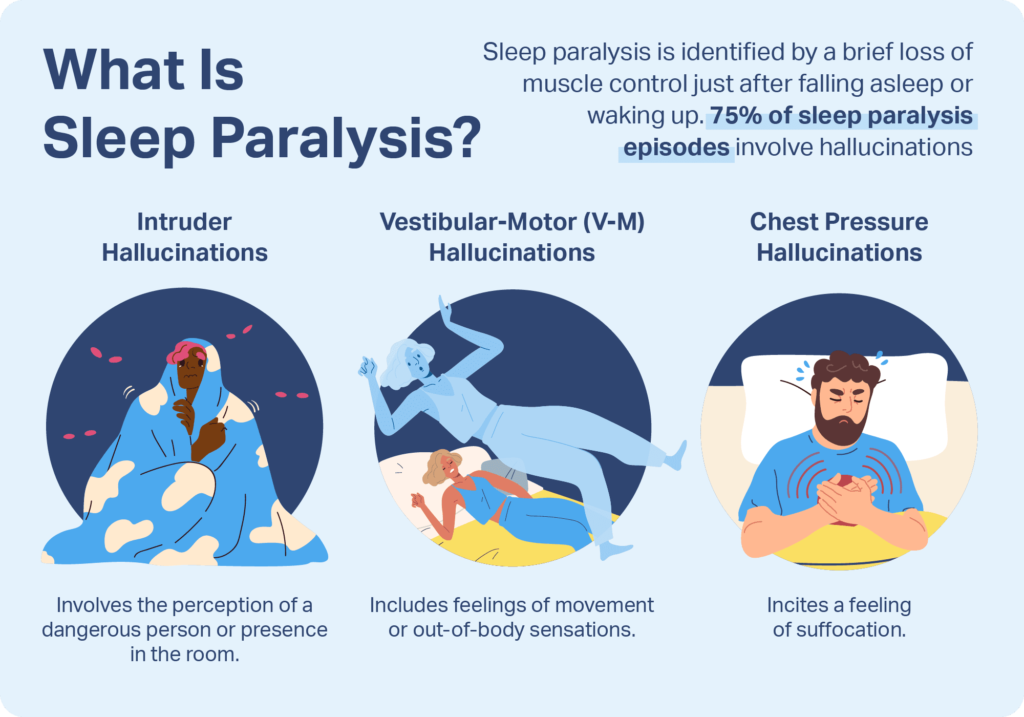
People experiencing sleep paralysis often report:
- A feeling of being trapped inside their own body
- A heavy pressure on their chest or throat
- A sense of danger or fear
- Hallucinations of ghostly figures, demons, or shadowy creatures
Though it can feel terrifying, sleep paralysis is not harmful and is usually a result of the brain misfiring during the sleep cycle.
What Happens to Your Brain During Sleep Paralysis?
Sleep paralysis occurs during the transition between REM sleep (Rapid Eye Movement) and wakefulness. Here’s what’s happening in your brain:
1. Your Brain Wakes Up, But Your Body Remains Paralyzed
During REM sleep, your brain is highly active, and this is when most dreaming occurs. To prevent you from acting out your dreams, your brain temporarily paralyzes your muscles—a process known as REM atonia.
However, in sleep paralysis, your brain wakes up before your body, leaving you temporarily trapped in a paralyzed state.
2. Your Amygdala Triggers a Fear Response
The amygdala is the part of the brain responsible for detecting threats and triggering fear responses. During sleep paralysis, the amygdala becomes overactive, making you feel like you’re in danger—even when no real threat exists.
3. Your Brain Creates Hallucinations
Many people report seeing shadowy figures, demons, or ghosts during sleep paralysis. These hallucinations occur because the brain is still in a dreamlike state while being partially awake. The mind tries to make sense of the paralysis, sometimes creating visual, auditory, or even physical sensations.
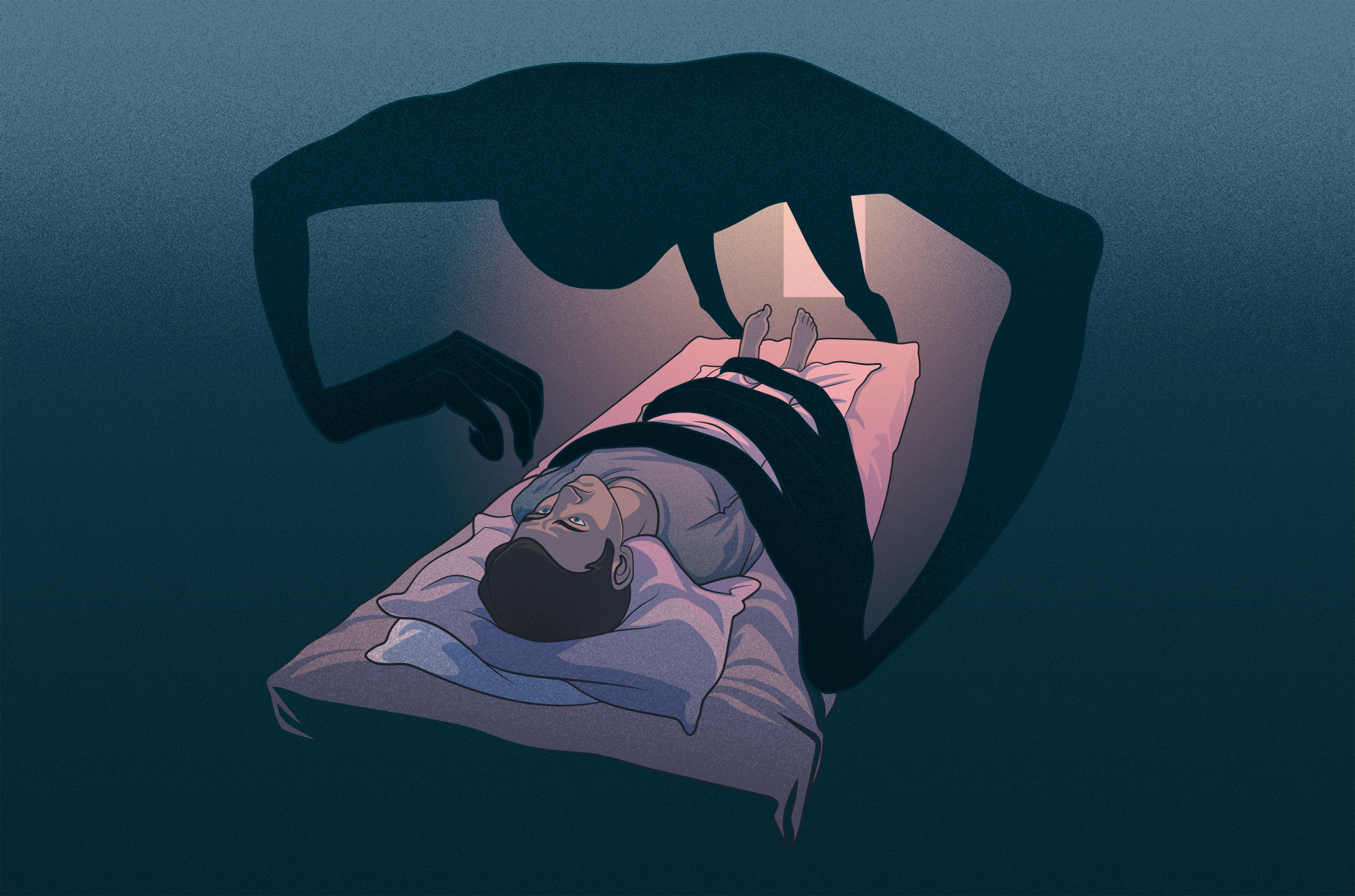

Causes of Sleep Paralysis
Several factors can trigger sleep paralysis, including:
- Sleep deprivation (not getting enough rest)
- Irregular sleep patterns (e.g., shift work, jet lag)
- Stress and anxiety
- Sleeping on your back (which can restrict breathing)
- Neurological conditions (such as narcolepsy)
How to Prevent Sleep Paralysis?
While sleep paralysis is not dangerous, it can be disturbing. Here are some ways to reduce the chances of experiencing it:
✅ Get enough sleep – Aim for 7-9 hours of quality rest per night.
✅ Maintain a regular sleep schedule – Try to go to bed and wake up at the same time daily.
✅ Reduce stress and anxiety – Practice meditation, deep breathing, or relaxation techniques before bed.
✅ Avoid sleeping on your back – Try sleeping on your side instead.
✅ Limit screen time before bed – Blue light from screens can disrupt sleep patterns.
Conclusion
Sleep paralysis is a fascinating yet frightening phenomenon that happens when the brain wakes up before the body. Though it can cause intense fear and hallucinations, it is not harmful. Understanding why it happens and how to prevent it can help reduce anxiety around the experience.







